Compliance Obligations for AML Risk Management
Discover the evolution of AML risk management in the EU, focusing on the EBA's guidelines and their impact on legal frameworks and financial institutions. Learn how these changes are strengthening defenses against financial crimes and enhancing the EU's financial system's integrity.

EBA Reporting Obligations for AML Risk Management Supervision

In accordance with Directive (EU) 2015/849's Article 48(10), the European Banking Authority (EBA) has published a crucial final report, designated as EBA/GL/2021/16. Comprehensive instructions on risk-based supervision, a crucial component of risk management for anti-money laundering (AML), are introduced in this paper. These rules, which demonstrate the EBA's determination to stop the funding of terrorism and money laundering, will go into effect on July 4, 2022. Moreover, important changes, as detailed in EBA/GL/2023/07, are slated to go into effect on December 30, 2024, which will be a big step forward in the development of AML risk management techniques.
- Guidelines Overview: A Cornerstone in AML Risk Management
The paper highlights the crucial role that competent authorities and financial institutions play in AML risk management by carefully outlining the responsibilities and reporting requirements for them. It highlights the fact that compliance is an essential component of efficient AML risk management as well as a legal need. - Integration into Operational Frameworks: EBA as a Blueprint
The European Banking Authority's guidelines function as a model for suitable supervisory procedures in the European System of Financial Supervision. They incentivize governing bodies to incorporate these techniques into their operational frameworks, which may require extensive alterations to current legal and regulatory frameworks. - Compliance Notification: Deadline and Implications
The notification and compliance status of relevant authorities are given a lot of weight. By May 30, 2022, they must notify the EBA of their compliance. The EBA will classify any failure to fulfill this deadline as non-compliant, underscoring the importance of prompt reporting in AML risk management. Prompt reporting of any future modifications to the compliance status is also required. - Strategic Framework for AML Risk Management
These recommendations go beyond simple regulations to provide a strategic framework that will improve AML risk management efficiency throughout European financial institutions. By following these recommendations, financial institutions and law enforcement agencies may play a vital role in preventing money laundering and terrorist funding, thereby preserving the integrity of the European financial system. A strong financial ecosystem that is resistant to unlawful activity depends critically on strict compliance, efficient reporting, and flexibility in response to changing AML risks.

Understanding AML Risk Management in the EU: EBA Guidelines Overview
The European Banking Authority (EBA) is largely responsible for the change in AML (Anti-Money Laundering) risk management procedures in the banking industry of the European Union. The EBA set a new standard for risk-based supervision with the release of guidelines EBA/GL/2021/16 and its later adjustments EBA/GL/2023/07. This change complies with the guidelines outlined in Directive (EU) 2015/849, Article 48(10). The following are these guidelines' main points:
- Comprehensive Framework: The guidelines offer a detailed framework for financial institutions, outlining necessary procedures and practices to combat money laundering and terrorist financing effectively.
- Alignment with EU Directives: These guidelines are in strict alignment with the EU’s broader regulatory framework, particularly Directive (EU) 2015/849, ensuring a consistent approach across all member states.
- Role of Financial Institutions and Authorities:
- Financial Institutions: They are required to implement these guidelines, incorporating them into their risk management and operational strategies.
- Competent Authorities: These bodies are tasked with overseeing the implementation and adherence to these guidelines, ensuring a uniform application across the sector.
- Commitment to Combating Financial Crimes: The EBA's guidelines reflect a strong commitment to safeguarding the EU's financial system from money laundering and terrorist financing activities.
- Risk-Based Supervision: A key focus of these guidelines is on risk-based supervision, which involves assessing and mitigating risks in a more targeted and efficient manner.
- Evolving Standards: The introduction of amendments under EBA/GL/2023/07 indicates that these guidelines are dynamic, evolving to meet the changing nature of financial crimes and risks.
By establishing these rules, the EBA improves on the present procedures for managing AML risks while also demonstrating its willingness to take the initiative to address potential problems in the banking industry down the road. The overall integrity and stability of the financial system of the European Union are greatly enhanced by this strategy.

Implementing EBA AML Risk Management Guidelines: A Detailed Roadmap
The implementation of the AML risk management recommendations by the European Banking Authority (EBA) on July 4, 2022, along with the ensuing modifications that take effect on December 30, 2024, represent a noteworthy advancement in the restructuring of the financial regulatory framework within the European Union. EBA/GL/2021/16 and EBA/GL/2023/07 provide precise rules that specify financial entities' duties and reporting criteria. This emphasizes the crucial relevance of compliance in the field of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) risk management.
- Integral Compliance in AML Risk Management: Beyond Formality
The rules emphasize compliance as essential to preserving the integrity and security of the financial system, going beyond simple statutory formalities. They encourage a proactive approach to AML risk management by laying forth specific responsibilities and reporting requirements for financial firms. - Strategic Blueprint for Financial Supervision: Integrating AML Practices
These recommendations lead the European System of Financial Supervision toward a more unified and integrated approach by acting as a strategic roadmap. They stress that these rules should not just be followed but also become ingrained in the regular operations of the financial system, and they support the smooth incorporation of AML practices into the operational frameworks of financial institutions. - Operational Integration: A Proactive AML Environment
In order to foster a more proactive and preventive AML environment within the European banking sector, integration is a crucial process. Financial institutions enhance the efficacy of recommendations by integrating anti-money laundering (AML) policies into their routine operations. This fosters a culture of alertness and minimizes risks.
The adoption of these rules and its continuous revisions represent a paradigm change in the EU's approach to AML risk management. It is a revolutionary framework—rather than merely a collection of regulations—that harmonizes real, integrated solutions with regulatory requirements to create a more stable and safe financial environment.
Impact of EBA's AML Risk Management Guidelines on Financial Institutions: A Paradigm Shift
The European Union's approach to risk management for anti-money laundering (AML) has undergone a radical change with the release of the European Banking Authority's (EBA) compliance guidelines. These recommendations, which place a strong emphasis on reporting and compliance requirements, demonstrate the EBA's steadfast dedication to combating money laundering and the funding of terrorism. This revolutionary change means that financial institutions across the EU must prioritize following these standards and make compliance a core component of their operating strategy.
- Serious Commitment to Eradication: Compliance as Core Strategy
The recommendations, which place a strong emphasis on compliance and reporting requirements, represent a serious commitment to ending illegal financial activity. It is now mandatory for financial institutions to incorporate compliance with these principles as a fundamental component of their operational strategy, promoting a responsible and vigilant culture in AML risk management. - Consequences of Non-Compliance: Impact on Reputation and Finances
Serious consequences could result from non-compliance, including regulatory proceedings like fines and punishments. The reputation and financial status of an institution may be severely impacted by these repercussions. Therefore, it is critical for financial institutions to carefully match their activities with the rules, both as a regulatory requirement and to protect their general stability. - Guidelines as Catalysts for Understanding and Integration
The recommendations facilitate a deeper understanding and integration of AML standards into the operational ethos of financial firms, going beyond their basic enforcement. The goal is to promote a proactive approach to risk mitigation by instilling a thorough awareness of AML principles, rather than only focusing on compliance.
Adopting these compliance principles is not just about satisfying regulatory requirements as financial institutions negotiate this paradigm change; it is also a strategic need to protect the financial industry from the threats of money laundering and terrorism financing. The rules are a revolutionary force in the European financial sector, propelling a cultural shift in AML risk management toward greater vigilance and resilience.

Transparency and Accountability in AML Risk Management
The guidelines set forward by the European Banking Authority (EBA) prioritize the enhancement of openness and accountability in the context of anti-money laundering (AML) risk management. For the financial sector to handle AML concerns in a dynamic and efficient manner, this focus is essential. Important elements consist of:
- Mandatory Compliance Notifications:
- Financial institutions are required to report their compliance status regularly.
- This ensures that all parties are consistently up-to-date with their AML obligations.
- Fostering Open Dialogue:
- The guidelines encourage open communication between regulatory authorities and financial entities.
- This collaboration is intended to create a more unified and effective approach to managing AML risks.
- Benefits of Increased Transparency:
- Enhanced transparency helps in identifying potential gaps and areas for improvement in AML practices.
- It facilitates better-informed decision-making by regulatory bodies and financial institutions alike.
- Accountability in Financial Operations:
- The guidelines hold financial institutions accountable for their AML practices.
- This accountability extends to ensuring that their operations are in strict adherence to the set AML standards.
- Collaborative Approach to AML Risks:
- By mandating these notifications, the EBA aims to cultivate a culture of shared responsibility in tackling AML issues.
- This approach recognizes that effective AML risk management is a collective effort involving multiple stakeholders.
- Impact on AML Strategies:
- The increased focus on transparency and accountability is expected to drive improvements in AML strategies.
- It encourages the adoption of more sophisticated and comprehensive AML measures.
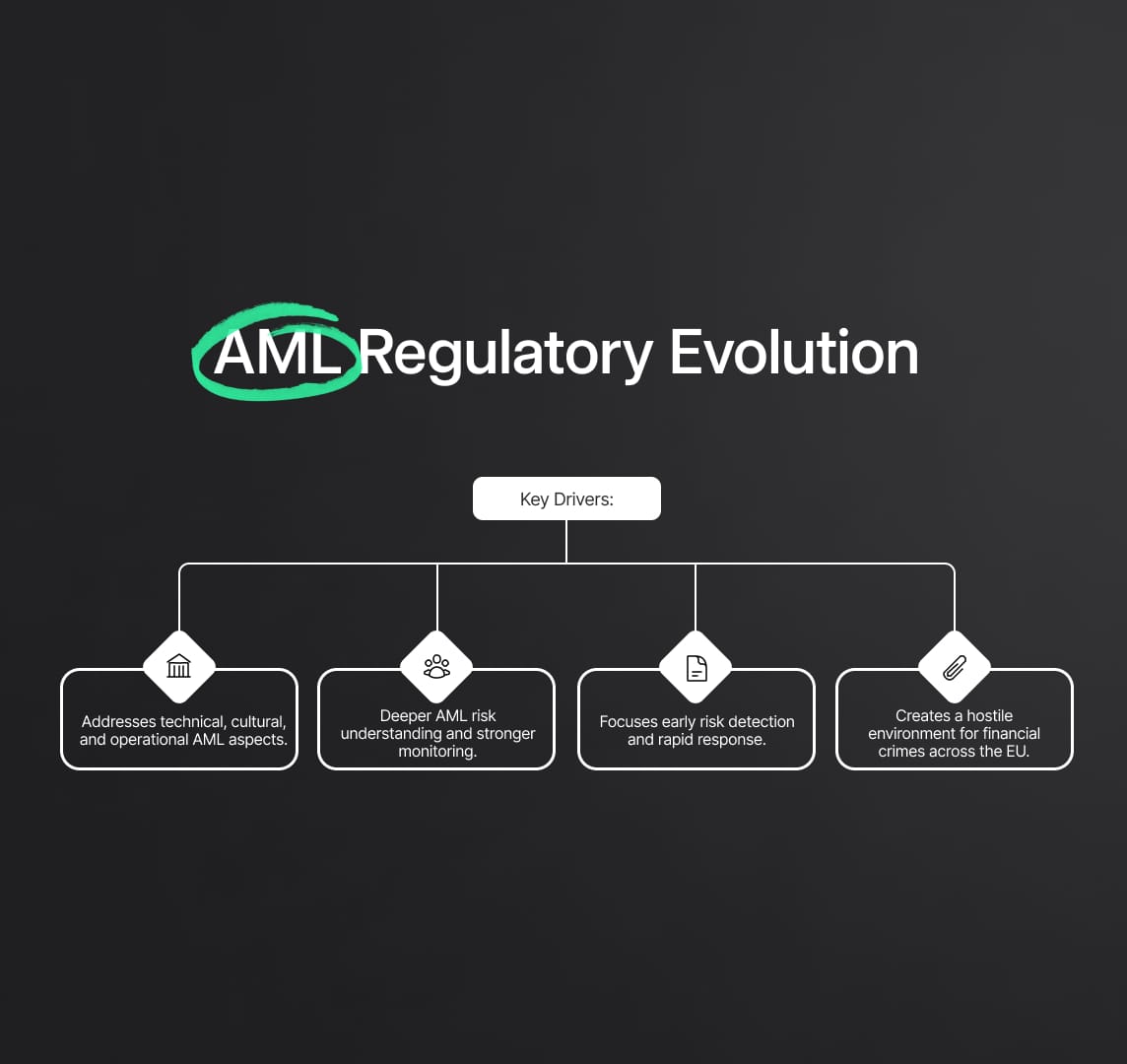
Evolution of Legal and Supervisory Frameworks in AML Risk Management
The legal and supervisory frameworks throughout the European Union (EU) have undergone a substantial evolution with the adoption of the European Banking Authority's (EBA) guidelines, particularly in the area of Anti-Money Laundering (AML) risk management. A proactive approach to bolstering defenses against financial crimes characterizes this dramatic development.
- Holistic Evolution Approach:
- Involves a holistic approach addressing technical, cultural, and operational aspects.
- Goes beyond procedural updates to instigate a comprehensive transformation.
- Operational Shift in Financial Institutions:
- Calls for operational shifts within financial institutions.
- Encourages a deeper understanding of AML risks and more rigorous monitoring.
- Proactive Risk Identification and Mitigation:
- Emphasizes a proactive approach to identify and mitigate AML risks.
- Expects financial institutions to be more vigilant and responsive in tackling financial crimes.
- Creating a Hostile Environment for Illicit Activities:
- Aims to make the EU's financial environment a hostile terrain for illicit activities.
- Expects the integration of guidelines to elevate the level of vigilance against financial crimes.
In conclusion, the approval of the EBA guidelines represents a comprehensive advancement in EU AML risk management rather than just a procedural update. The preventive steps made are intended to build a financial environment that is resistant to illegal financial activity in addition to being strong and efficient.

Safegarding the EU Financial System through Enhanced AML Risk Management
To sum up, the instructions provided by the European Banking Authority (EBA) for managing the risk of money laundering (AML) surpass simple regulatory requirements. They stand for a strategy framework designed to dramatically improve the efficiency of European financial institutions' efforts to prevent money laundering and the funding of terrorism.
- Strategic Framework for Effectiveness:
- Represents a strategic framework designed to enhance the effectiveness of AML efforts.
- Goes beyond regulatory directives to establish a comprehensive approach.
- Crucial Step for Financial System Integrity:
- The adoption of these guidelines is a crucial step in ensuring the integrity and robustness of the EU’s financial system.
- Signifies a commitment to maintaining a secure financial environment.
- Setting Standards for Compliance and Innovation:
- Sets standards not only for compliance but also for innovation in AML risk management.
- Encourages the adoption of advanced technologies to stay ahead of sophisticated financial crimes.
- Preparedness for Future Challenges:
- The strategic framework prepares financial institutions for future challenges in financial security.
- Positions the EU to respond not just to current threats but also to emerging risks in the financial landscape.
- Reinforcing EU’s Reputation:
- In embracing these guidelines, the EU strengthens defenses against illicit financial activities.
- Reinforces the EU's reputation as a secure and trustworthy financial market.
- Broader Impact on Economy and Society:
- Essential for the stability of the financial sector.
- Fosters a climate of trust and security in the EU's financial system, benefiting the broader economy and society.
In conclusion, the EU's financial landscape is becoming more robust and safe with the implementation of the EBA's AML guidelines. It emphasizes the significance of remaining proactive in the face of changing financial threats and lays the groundwork for both compliance and innovation.
Reduce your
compliance risks

