EMIR Regulation: FCA’s Consultation for UK Trade Repositories
FCA consults on proposed EMIR regulation guidance, focusing on data validation, reporting standards, and compliance for UK trade repositories.

The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) has launched a consultation on proposed guidance for UK trade repositories (TRs) registered under the UK European Market Infrastructure Regulation (UK EMIR), which aims to address critical operational and technical challenges faced by TRs ahead of the new reporting requirements effective from 30 September 2024.
This guidance, developed in collaboration with the Bank of England, focuses on data validation, submission processes, and compliance with EMIR regulation, emphasising the need for TRs to adapt to updated schemas, manage legacy data, and ensure precise reporting through rigorous validation standards. The changes impact how TRs handle both old and new formats, validate lifecycle events, and fulfill specific reporting obligations, significantly enhancing data quality and regulatory compliance within the EMIR framework. This consultation underscores the FCA’s commitment to refining the UK EMIR framework, ensuring TRs and counterparties are well-prepared for the evolving regulatory landscape.
Source
[1]

[2]
Overview of EMIR Regulation
The European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR) was introduced by the European Union to enhance transparency and reduce systemic risks in over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives markets, especially after the 2008 financial crisis. Following Brexit, the UK retained its version of EMIR, known as UK EMIR, which is a cornerstone of the UK's regulatory framework. UK EMIR imposes stringent reporting, clearing, and risk mitigation requirements on derivatives transactions, requiring TRs to serve as central data hubs responsible for collecting, validating, and maintaining transaction data to ensure market transparency and compliance with EMIR regulation standards.
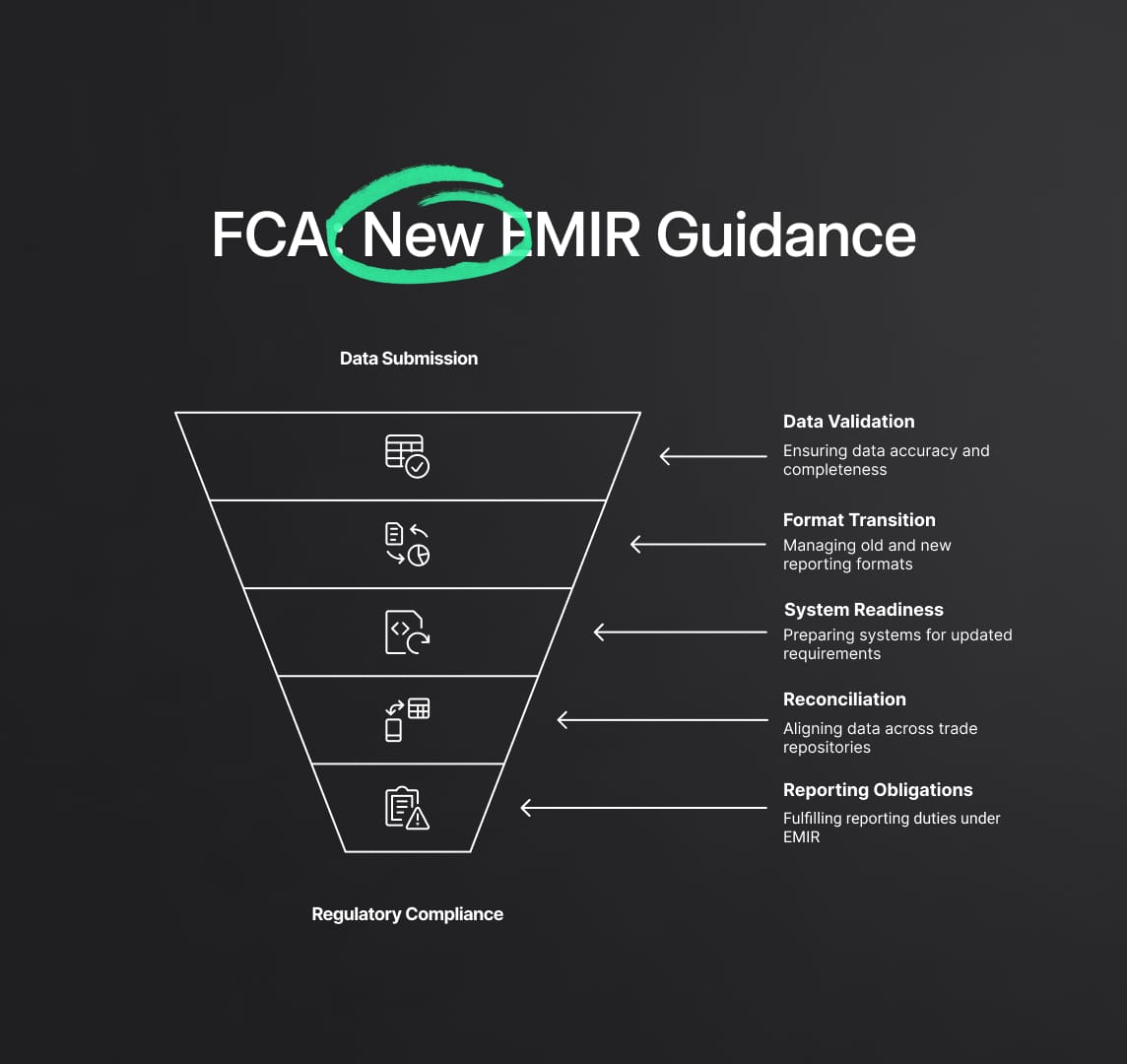
Details of the FCA's Proposed Guidance on European Market Infrastructure Regulation
The FCA’s proposed guidance was developed in response to requests from UK TRs to address specific operational challenges as they transition to updated UK EMIR reporting requirements. The guidance is structured in a question-and-answer format, providing clear instructions on critical aspects such as data validation, operational practices, and reconciliation processes under EMIR regulation.
1. Data Validation and Reporting Requirements
- Validation of Data Fields: The guidance under EMIR regulation specifies detailed criteria for validating data fields in submitted reports, including acceptable formats, error handling procedures, and data rejection criteria. TRs must ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency, which are crucial for effective market oversight and compliance with EMIR regulation. The guidance emphasizes sequencing lifecycle events using fields like Event Date, Action Type, and Event Type, ensuring chronological accuracy in derivatives reporting.
- Handling Old and New Formats: TRs are required under EMIR regulation to include both old and new formats of derivative reports in Trade State Reports (TSRs) during the transition period. This dual-format approach ensures continuous data availability for regulatory authorities as reporting standards evolve. TRs must include legacy data alongside updated formats in TSRs, ensuring comprehensive market data access throughout the transition phase.
- Processing Lifecycle Events: EMIR regulation mandates that TRs validate lifecycle events based on a specific sequence derived from Event Date, Action Type, and Event Type fields. This structured validation process ensures accurate reporting of changes in derivative transactions. When multiple lifecycle events occur on the same day, TRs must use valuation and margin timestamps to determine the correct order of events, maintaining the integrity of reported data.
2. Operational Practices for Trade Repositories
- System Readiness and Transition Management: Under EMIR regulation, TRs must ensure their systems are fully equipped to handle updated reporting requirements, including the ability to process both current and new formats during the transition. The guidance emphasizes rigorous system testing and coordination with counterparties to mitigate operational disruptions. TRs are encouraged to engage in thorough testing of data validation rules and collaborate with market participants to resolve issues proactively.
- Publication of Aggregate Data: In compliance with Article 1 of Technical Standards 151/2013 under EMIR regulation, TRs are required to publish aggregated data. During the six-month transition period, TRs should provide a unified version of aggregated data that includes both current and updated UK EMIR reporting formats, ensuring data consistency and accessibility for regulatory purposes. Following the transition, TRs must publish aggregated data exclusively in the updated reporting format to meet EMIR regulation requirements.
- Error Handling and Rejection Messages: EMIR regulation specifies that TRs must provide immediate rejection feedback within 60 minutes of data receipt and issue end-of-day reports by 09:00 UTC the following working day. This dual approach ensures that counterparties can promptly address and rectify errors, maintaining the quality of reported data. Detailed rejection messages should include specific error codes and descriptions to facilitate understanding and correction of issues by reporting entities.
3. Reconciliation and Reporting Obligations
- Inter-TR Reconciliation: During the transition period, EMIR regulation instructs TRs to use a relaxed schema for inter-TR reconciliations due to the coexistence of both current and updated reports. Post-transition, TRs must adopt a strict schema exclusively for the updated reporting format, ensuring precise alignment and reconciliation across trade repositories. The guidance requires TRs to manage the reconciliation process diligently, resolving any discrepancies between TRs swiftly to uphold data integrity under EMIR regulation.
- Managing Legacy Data: For derivatives reported under previous standards, EMIR regulation requires TRs to ensure accurate and up-to-date reporting during the transition to the new requirements. TRs must maintain historical trade activity reports, which are critical for ongoing regulatory monitoring. The guidance specifies that if certain data blocks fail schema validation, TRs should exclude only the non-compliant data rather than omitting entire records, ensuring that legacy data remains available for regulatory review.
- Schema Adaptations for Transition: Under EMIR regulation, TRs must utilize specific schemas during and after the transition period. The relaxed schema (RELAXEDauth.091.001.02_FCAUG_DATREC_1.0.0) is mandated during the transition to accommodate both updated and legacy reports. After the transition, TRs are required to switch to the strict schema (auth.091.001.02_FCAUG_DATREC_1.0.0) to ensure full compliance with the updated EMIR regulation reporting standards, enhancing the accuracy and regulatory usefulness of reported data.
4. EMIR Specific Reporting Obligations and Delegations
- Reporting Obligations: Under EMIR regulation, all counterparties must report any derivative contract concluded, modified, or terminated. Both counterparties are required to report their side of the trade unless a prior arrangement exists allowing one party to report on behalf of both. Financial counterparties are solely responsible for reporting on behalf of both themselves and non-financial counterparties when required by EMIR regulation, ensuring that data integrity and completeness are maintained.
- Delegation of Reporting: Counterparties may delegate their reporting obligations under EMIR regulation to third parties, such as central counterparties or trading platforms. However, the details reported must include the full set of information that would have been reported had each counterparty submitted their reports separately. The responsibility and legal liability for the accuracy of the reported data remain with the delegating counterparty.
- Use of Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs): EMIR regulation requires all UK counterparties to have a Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) for derivative trades. LEIs must be obtained from Local Operating Units (LOUs) accredited by the Global LEI Foundation (GLEIF). The use of LEIs ensures standardization and traceability of reported transactions, enhancing transparency and regulatory oversight.
- Intragroup Reporting Exemptions: Derivative contracts within the same group, where at least one counterparty is a non-financial counterparty, may be exempt from the reporting obligation if specific conditions are met. TRs and counterparties must notify the FCA if they intend to use this exemption, ensuring regulatory awareness and compliance with EMIR regulation standards.
UK EMIR reporting requirements: Implications for UK Trade Repositories and Market Participants
The FCA’s proposed guidance provides UK TRs with the critical tools needed to comply with the new UK EMIR reporting requirements, focusing on robust data validation, operational preparedness, and consistent reporting practices under EMIR regulation. For counterparties, the guidance offers essential clarity on reporting obligations and the standards required to maintain compliance, ensuring that data submissions meet the high expectations set by EMIR regulation. TRs must engage in extensive testing, develop data management strategies, and foster industry collaboration to achieve these regulatory standards.
The FCA’s collaborative approach, which includes engaging with TRs, counterparties, trade associations, law firms, and consultants, ensures that the guidance is practical, addresses real-world operational challenges, and supports a smooth transition to the updated UK EMIR framework. By working closely with these stakeholders, the FCA aims to enhance data quality, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance within the EMIR regulation landscape.
Reduce your
compliance risks


