Financial Compliance Management: What is it?
Comprehensive overview of Financial Compliance Management, highlighting regulatory adherence, risk mitigation, ethical governance, digital transformation with RegTech, and best practices essential for financial institutions.

Financial Compliance Management is a systematic and rigorous framework through which financial institutions ensure comprehensive adherence to applicable legal, regulatory, and ethical standards governing their financial activities and transactions. It includes an extensive spectrum of obligations covering diverse segments of the financial industry, such as investment banking, retail banking, asset management, insurance, and brokerage services.
The primary objective of financial compliance management is to safeguard the integrity and transparency of financial systems, actively prevent fraudulent activities, mitigate regulatory risks, and uphold robust ethical conduct. This is achieved through continuous compliance audits, meticulous regulatory reporting, rigorous internal controls, and the consistent alignment of institutional practices with prevailing legal frameworks, regulatory requirements, and established industry standards.
Consequently, financial compliance management emerges as an indispensable component for any financial institution aiming to sustain operational integrity, regulatory credibility, and stakeholder trust in a complex and evolving financial environment.
Understanding Financial Compliance Management
Financial compliance management constitutes a critical and sophisticated discipline within the financial services industry, fundamental to ensuring the integrity, stability, and efficiency of financial markets. It involves systematic and rigorous procedures by which financial institutions meticulously align their operations and transactions with an extensive array of evolving laws, regulations, and supervisory guidelines.
At its foundation, financial compliance management fulfills several crucial roles:
- Regulatory Adherence: Comprehensive compliance requires detailed adherence to intricate financial regulations, including but not limited to the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), Basel III accords, MiFID II, and directives from prominent regulatory bodies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA), Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
- Risk Mitigation: Institutions systematically identify, analyze, and proactively mitigate potential compliance risks. Effective risk management practices prevent substantial regulatory fines, significant legal repercussions, operational interruptions, and reputational damage, thereby ensuring institutional resilience and market trust.
- Ethical Standards Enforcement: Maintaining rigorous ethical standards is essential for securing the trust of all stakeholders—customers, investors, regulatory authorities, and the broader public. Ethical compliance underpins corporate responsibility and reinforces the institution's commitment to integrity and transparency.
For financial institutions, compliance management transcends legal necessity and serves as a strategic enabler. It drives operational excellence by enhancing efficiency, reducing exposure to compliance-related financial liabilities, and bolstering institutional credibility. Given its inherently dynamic nature, institutions must continuously adapt their compliance strategies to respond effectively to an ever-changing regulatory environment.
Financial compliance management addresses several critical compliance domains:
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML): Robust implementation of AML frameworks and sophisticated transaction-monitoring systems that proactively detect and prevent illicit financial activities, in alignment with global standards like FATF recommendations.
- Know Your Customer (KYC): Comprehensive customer due diligence and identity verification procedures, designed to mitigate fraud risk, support appropriate financial product suitability, and ensure adherence to AML and counter-terrorist financing (CTF) regulations.
- Insider Trading Prevention: Implementation of stringent internal controls and monitoring systems to prevent unauthorized trading activities based on material non-public information, maintaining market integrity and fairness.
- Data Protection Compliance: Rigorous adherence to data protection frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and other jurisdiction-specific data privacy regulations, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and secure availability of sensitive customer information.
- Cybersecurity Frameworks: Deployment of comprehensive cybersecurity protocols designed to protect financial infrastructure against cyber threats, safeguard sensitive data from breaches, and ensure operational continuity in compliance with cybersecurity standards such as NIST Cybersecurity Framework and ISO/IEC 27001.

The Imperative of Financial Compliance Management
The imperative of financial compliance management in the banking and financial sector cannot be understated. It ensures the adherence of financial institutions to a complex array of regulatory and legal requirements, safeguarding the economy, protecting consumers, and maintaining the integrity of the financial markets.
The primary objectives of financial compliance management include:
- Maintaining Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up-to-date with the plethora of financial regulations and laws is essential to avoid legal sanctions and financial penalties.
- Risk Management: By proactively managing and mitigating compliance risks, financial institutions can prevent operational disruptions and protect their reputations.
- Promoting Ethical Practices: Compliance management enforces ethical business practices, which are crucial for maintaining customer and investor trust.
The consequences of failing to manage compliance effectively can be severe, ranging from financial penalties to the loss of banking licenses, not to mention the potential for significant reputational damage. Non-compliance can erode customer confidence and investor trust, which are the lifeblood of any financial institution.
An effective financial compliance management system involves:
- Risk Identification and Assessment: Financial institutions must continuously identify and evaluate compliance risks as part of their risk management strategy.
- Regulatory Change Management: Keeping pace with regulatory changes and adapting compliance programs accordingly is essential to avoid becoming outdated.
- Compliance Training and Awareness: Ensuring that all employees, from front-line staff to senior management, are aware of compliance requirements and understand how to fulfill them.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Implementing systems to monitor compliance and report breaches or potential breaches to regulatory authorities.
- Compliance Audits: Conducting regular audits to assess the effectiveness of compliance programs and identify areas for improvement.
Establishing an Effective Compliance Management Framework
A robust and effective financial compliance management framework is foundational for ensuring the operational integrity, regulatory adherence, and strategic resilience of financial institutions. Such a framework encompasses an integrated approach involving Governance, Risk Management, and Compliance (GRC), which is critical to managing complex regulatory requirements and proactively addressing compliance-related challenges.
Governance Structure:
- Leadership by Chief Compliance Officer (CCO): The CCO is integral to establishing a compliance-oriented organizational culture, setting clear standards and expectations, and providing strategic oversight across compliance processes. This senior leadership role ensures the coherence, effectiveness, and transparency of compliance initiatives.
- Active Board Involvement: The board of directors holds ultimate accountability, providing strategic oversight and ensuring alignment between compliance strategies and broader corporate objectives. Their involvement reinforces accountability, allocates adequate resources, and validates the institution’s commitment to compliance at the highest organizational levels.
- Defined Roles and Responsibilities: Precise delineation and communication of compliance responsibilities across all organizational levels are imperative. Clearly defined roles ensure that staff understand their individual compliance duties, significantly reducing the risk of regulatory breaches through misunderstanding or oversight.
Risk-Based Compliance:
- Strategically Tailored Compliance Initiatives: Adopting a risk-based compliance framework allows financial institutions to prioritize resources effectively, targeting regulatory areas that present the highest risks of non-compliance. Such an approach optimizes resource allocation, enhances compliance efficiency, and strategically mitigates significant institutional vulnerabilities.
- Continuous and Dynamic Risk Assessment: Constantly evolving regulatory landscapes require financial institutions to undertake ongoing compliance risk assessments. Utilizing robust risk assessment tools and methodologies ensures proactive identification, evaluation, and adjustment of compliance strategies, maintaining agility and responsiveness to regulatory changes and emerging risks.
Integration into Business Processes:
- Embedding Compliance in Core Processes: Effective compliance demands seamless integration into all critical business operations, ensuring compliance considerations are inherently embedded within institutional workflows and decision-making processes. This integration minimizes operational disruptions, streamlines compliance execution, and promotes consistent adherence across the organization.
- Comprehensive Employee Training Programs: Continuous and targeted training programs ensure that all employees remain well-informed regarding compliance requirements, regulatory developments, and internal compliance policies. Regular, tailored training enhances employee competence, reduces compliance risk exposure, and reinforces organizational commitment to regulatory adherence.
- Leveraging Advanced Technology Solutions: Utilizing sophisticated compliance management technologies, such as automated compliance monitoring systems, RegTech platforms, and data analytics tools, significantly streamlines compliance operations. These advanced technologies minimize human error, enhance compliance accuracy, provide real-time compliance monitoring, and facilitate effective reporting and audit processes.
Essential Components for Comprehensive Compliance
In addition to governance, risk management, and integration strategies, a fully effective financial compliance framework should include:
- Robust Internal Controls: Comprehensive internal control mechanisms designed to identify, prevent, and promptly rectify compliance deficiencies, thereby reducing institutional risk exposure.
- Regular Compliance Assessments and Audits: Frequent internal assessments and periodic external audits provide objective validation of compliance effectiveness, identifying potential gaps and facilitating continuous improvements.
- Transparent Reporting and Disclosure Mechanisms: Clear, accurate, and timely communication of compliance status to stakeholders fosters institutional transparency, trust, and accountability, ensuring stakeholders are consistently informed of the institution’s compliance posture.

The Digital Transformation of Financial Compliance Management
The digital transformation of financial compliance management represents a pivotal shift in the financial services sector, fundamentally reshaping compliance strategies through the integration of advanced technologies, sophisticated analytics, and agile methodologies. This transformation significantly enhances operational efficiency, accuracy, regulatory responsiveness, and the proactive management of compliance risks.
RegTech Solutions:
- Advanced Regulatory Compliance: RegTech (Regulatory Technology) solutions encompass specialized digital platforms and applications explicitly designed to streamline and enhance regulatory compliance management. These tools facilitate automated monitoring, real-time compliance reporting, efficient management of complex regulatory requirements, and reduction in manual compliance tasks, thereby significantly reducing human error and improving overall compliance accuracy.
- Enhanced Adaptability: A key strength of RegTech solutions is their inherent flexibility and rapid adaptability to regulatory changes. Through automated updates, configurable workflows, and scalable infrastructures, financial institutions can swiftly accommodate new or evolving regulatory demands, maintaining continuous compliance without disruption.
Data-Driven Compliance:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing sophisticated data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence, institutions can proactively anticipate potential compliance breaches and identify high-risk areas before incidents occur. Predictive analytics empowers compliance teams with actionable foresight, enabling preemptive interventions that mitigate compliance risks and avert potential regulatory penalties.
- Actionable Insight Generation: Advanced analytics provide in-depth insights into compliance performance and effectiveness, systematically identifying areas requiring attention, optimization, or resource reallocation. Such analytical capabilities support evidence-based decision-making and continuous improvement of compliance frameworks, directly enhancing institutional effectiveness and regulatory assurance.
The Seven Elements of a Comprehensive Financial Compliance Management Program
A comprehensive financial compliance management program is built upon seven foundational elements. These elements ensure that financial institutions have a robust and responsive compliance framework that can adapt to the changing regulatory landscape.
Policies and Procedures:
- Documentation: The foundation of any compliance program is the documentation of clear policies and procedures.
- Accessibility: These documents should be easily accessible to all employees and regularly updated to reflect current regulations.
Oversight and Governance:
- Compliance Officers: Designated compliance officers and committees are tasked with monitoring compliance efforts and reporting to the board of directors.
- Accountability: These individuals must have the authority to enforce compliance measures and hold employees accountable.
Training and Education:
- Continuous Learning: Regular training is essential to ensure that employees understand their compliance responsibilities.
- Relevance: Training programs should be relevant to the specific roles of employees and updated to reflect the latest regulatory developments.
Communication and Reporting:
- Reporting Mechanisms: There must be clear mechanisms in place for employees to report potential compliance issues.
- Protection from Retaliation: Employees should feel safe to report concerns without fear of retaliation.
Monitoring and Auditing:
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuous monitoring is necessary to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Independent Audits: Periodic independent audits provide an objective assessment of the compliance program's effectiveness.
Enforcement and Discipline:
- Clear Consequences: There should be clear consequences for non-compliance to emphasise the importance of adherence to compliance protocols.
- Consistent Application: Disciplinary measures should be consistently applied across the business.
Corrective Action and Improvement:
- Timely Response: When compliance issues are identified, there must be a process in place to take corrective action promptly.
- Preventive Measures: The institution should also implement preventive measures to avoid future compliance issues.

The Decision Between Building or Buying Compliance Management Softwares
When it comes to compliance software, financial institutions face a strategic decision: build a bespoke system in-house or buy a pre-existing solution. Each option carries its own set of benefits and challenges, and the decision can significantly impact the institution's compliance operations.
Building Custom Compliance Software:
- Customisation: Building custom software allows for tailoring features specifically to the institution's needs, potentially offering a perfect fit for unique compliance processes.
- Integration: Custom solutions can be designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems and workflows.
- Control: Owning the software gives the institution full control over the development roadmap, with the ability to prioritize features and updates.
Challenges of Building Software:
- Resource Intensive: Developing software in-house requires significant investment in time, expertise, and money.
- Ongoing Maintenance: The institution must commit to maintaining and updating the software, which can become a continuous drain on resources.
Buying Pre-Existing Compliance Software:
- Quick Implementation: Off-the-shelf solutions can be deployed quickly, allowing institutions to benefit from enhanced compliance management without delay.
- Proven Solutions: Established software has been tested across different scenarios, providing reliability and a track record of performance.
- Support and Updates: Vendors typically offer ongoing support and regular updates to ensure the software stays current with regulatory changes.
Challenges of Buying Software:
- Less Tailored: Pre-built software may not fit every institution's specific needs perfectly and can require adjustments or workarounds.
- Dependency on Vendor: The institution becomes dependent on the vendor for critical updates and support, which may impact long-term flexibility.
The decision between building or buying will be influenced by factors such as the institution's size, complexity of compliance needs, in-house technical capabilities, and strategic priorities. In many cases, a combination of both—augmenting a purchased system with custom-built features—may offer the best of both worlds.

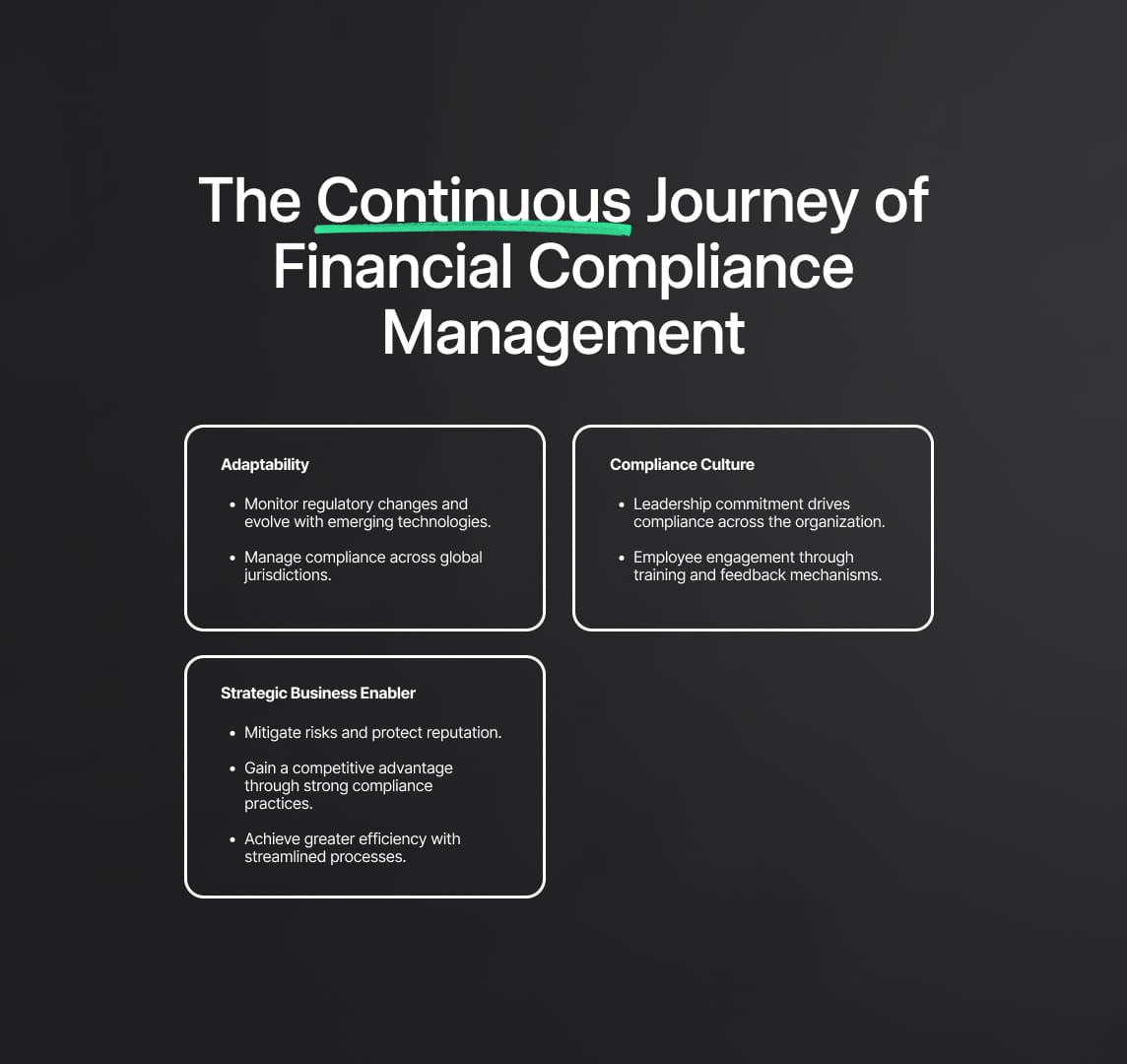
The Continuous Journey of Financial Compliance Management
The journey of financial compliance management is an ongoing one, shaped by a constantly evolving regulatory landscape and the necessity for institutions to adapt their practices accordingly. This journey is marked by the need for vigilance, adaptability, and a proactive mindset.
Adaptability and Continuous Improvement:
- Regulatory Changes: Financial institutions must continuously monitor for changes in regulations and adapt their compliance programs accordingly.
- Technology Advancements: As new technologies emerge, compliance programs must evolve to address the new risks and opportunities they present.
- Globalisation: Financial institutions operating globally must manage compliance across different jurisdictions with varying regulatory requirements.
Maintaining a Compliance Culture:
- Top-Down Leadership: Senior management must lead by example, demonstrating a commitment to compliance that permeates the entire organisation.
- Employee Engagement: Engaging employees in compliance training and awareness programs helps to embed compliance into the organizational culture.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Encouraging feedback from employees can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of compliance practices and identify areas for improvement.
Strategic Compliance as a Business Enabler:
- Risk Mitigation: Effective compliance management mitigates risks, preventing financial penalties and protecting the institution's reputation.
- Competitive Advantage: A strong compliance record can serve as a competitive advantage, positioning the institution as a leader in ethical business practices.
- Operational Efficiency: Streamlined compliance processes can lead to greater operational efficiency, reducing the costs and resources associated with managing compliance.
The Strategic Value of Financial Compliance Management
Compliance management in the financial sector goes beyond fulfilling legal obligations; it's a strategic function that underpins the ethical framework and operational integrity of an organisation. In a world where consumers are increasingly aware and regulators ever-vigilant, the strategic value of robust financial compliance management is clear.
Trust and Reputation Management:
- Consumer Confidence: Adherence to compliance standards fosters consumer confidence and loyalty.
- Investor Attraction: Investors are more likely to engage with institutions that demonstrate a commitment to compliance and ethical operations.
- Regulatory Relationships: A strong compliance record can lead to more favorable relationships with regulators, often resulting in a more collaborative approach to compliance and regulation.
Operational Advantages:
- Efficiency Gains: By integrating compliance management into operational processes, institutions can gain efficiencies and reduce the risk of compliance breaches.
- Risk Management: Proactive compliance management serves as a risk management tool, identifying potential areas of risk before they become issues.
- Decision Support: Compliance data can provide valuable insights that support strategic decision-making and business planning.
Strategic Decision-Making:
- Market Positioning: Compliance management can influence strategic decisions about market positioning, product development, and service offerings.
- Risk Appetite: Understanding the institution's compliance capabilities can inform the risk appetite and strategic direction of the business.
- Business Growth: Compliance management can support business growth by ensuring that new initiatives are launched with a clear understanding of the regulatory requirements.
Reduce your
compliance risks

