From the AML Framework to AMLA Establishment: EBA's Role
he European Banking Authority (EBA) welcomes the new EU anti-money laundering framework effective from 26 June 2024. The EBA will maintain its AML/CFT powers until December 2025, supporting Member States and the new AMLA.

Introduction
On June 26, 2024, the European Banking Authority (EBA) issued a pivotal press release announcing the implementation of the new EU Anti-Money Laundering (AML) framework. This landmark development marks a significant step forward in the EU's ongoing efforts to combat money laundering and counter the financing of terrorism (CFT). This article delves into the technical details of the new framework, the roles and responsibilities of the EBA and the newly established Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA), and the implications for financial institutions across Europe.
Source
[1]

[2]
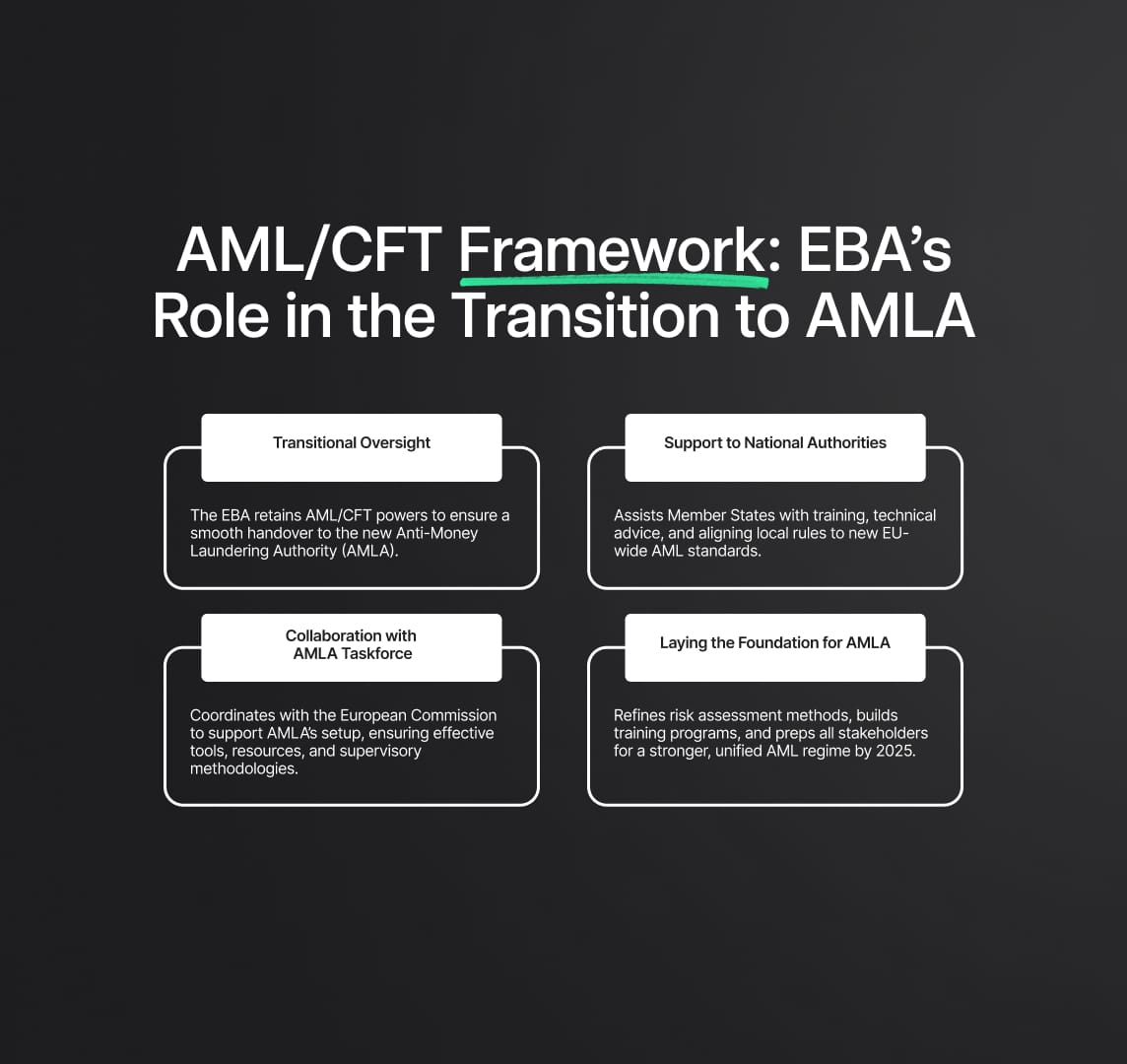
AML/CFT Framework: The Role of the European Banking Authority (EBA)
The EBA has been at the forefront of AML/CFT efforts within the EU since 2020. With the new AML framework, the EBA will continue to wield its AML/CFT powers and mandates until December 2025 to ensure a seamless transition. During this period, the EBA will collaborate closely with AMLA and provide crucial support to Member State competent authorities.
Key Responsibilities During the Transition Phase
- Support for Member State Authorities: The EBA will assist national authorities in preparing for the integration of AMLA, ensuring a unified and coordinated approach to AML/CFT efforts. This includes providing technical assistance, sharing best practices, and facilitating training programs to enhance the capabilities of national supervisors in combating money laundering and terrorist financing. The EBA will also help in aligning national regulations with the new EU-wide standards to ensure uniformity and consistency in AML/CFT measures across the Union.
- Coordination with the European Commission’s AMLA Taskforce: The EBA will play a central role in harmonizing efforts across the EU, working in tandem with the European Commission to streamline processes and enhance efficiency. This involves participating in the AMLA taskforce, which is responsible for the establishment and operational setup of AMLA. The EBA’s coordination efforts will focus on ensuring that AMLA is equipped with the necessary tools, resources, and methodologies to effectively oversee and enforce AML/CFT regulations.
The EBA's continued involvement during this critical transition phase ensures that the shift towards the new AML framework is smooth and minimally disruptive to existing AML/CFT operations. By maintaining its regulatory oversight and advisory roles, the EBA aims to bolster the overall integrity of the financial system and enhance the EU’s defenses against financial crime.
The transition phase is crucial as it sets the groundwork for the operational success of AMLA. The EBA's tasks include refining the methodologies for risk assessment and supervision, developing comprehensive training programs for national authorities, and ensuring that all stakeholders are prepared for the enhanced regulatory environment. By the end of 2025, when the EBA’s AML/CFT mandates are fully transferred to AMLA, the new authority will be positioned to take over seamlessly and continue the robust oversight required to combat money laundering and terrorist financing effectively.
AML/CFT Priorities for 2024-2025
Over the next two years, the European Banking Authority (EBA) will focus on several critical areas to bolster the EU's Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Countering the Financing of Terrorism (CFT) regime. These priorities are designed to enhance the overall effectiveness of AML/CFT measures and ensure a robust framework capable of addressing both current and emerging threats. The EBA's strategic approach will encompass the following key areas:
Methodology for Selecting Financial Institutions for Direct Supervision
One of the paramount tasks for the EBA is developing a comprehensive methodology for identifying financial institutions that will be subject to direct EU-level AML/CFT supervision. This methodology will involve a multi-faceted risk assessment process that includes:
- Risk Profiling: Establishing detailed criteria for evaluating the risk profiles of financial institutions based on their geographic location, customer base, transaction volumes, and historical compliance records.
- Data Integration: Leveraging data from various sources, including financial transactions, regulatory filings, and intelligence reports, to create a holistic view of each institution's risk level.
- Algorithmic Assessment: Utilizing advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms to continuously assess and update the risk profiles, ensuring that high-risk institutions are promptly identified and monitored.
Common Risk Assessment Methodology
To standardize risk evaluations across different jurisdictions, the EBA will establish a common risk assessment framework. This framework will:
- Uniform Risk Indicators: Define a set of standardized risk indicators that all EU member states will use to assess AML/CFT risks. These indicators will cover various aspects such as transaction anomalies, customer behaviors, and sector-specific risks.
- Scoring Systems: Implement a unified scoring system that quantifies the risk levels of financial institutions, facilitating easier comparison and assessment across the EU.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: Promote information sharing and collaboration between national regulators to ensure that risk assessments are consistent and comprehensive. This includes establishing protocols for regular updates and feedback mechanisms to refine the risk indicators and scoring systems.

Customer Due Diligence (CDD) Requirements
The EBA will define rigorous Customer Due Diligence (CDD) requirements to ensure thorough verification and monitoring of customers. Key elements will include:
- Identification Protocols: Standardizing the information required for customer identification, including biometric data, proof of address, and financial history.
- Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD): Implementing enhanced due diligence measures for high-risk customers, such as politically exposed persons (PEPs), customers from high-risk jurisdictions, and those involved in large or unusual transactions.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Establishing continuous monitoring protocols to detect and report suspicious activities. This will involve the use of real-time data analytics and automated alert systems to flag potential AML/CFT violations.
Criteria for Determining the Seriousness of AML/CFT Breaches
To ensure appropriate and proportional responses to AML/CFT breaches, the EBA will establish clear criteria for assessing the seriousness of violations. This will include:
- Breach Classification: Categorizing breaches based on their severity, ranging from minor procedural lapses to significant systemic failures.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluating the potential impact of breaches on the financial system, including financial losses, reputational damage, and the potential facilitation of criminal activities.
- Sanction Guidelines: Developing guidelines for imposing sanctions and administrative measures, ensuring that penalties are proportionate to the severity of the breaches. This will include monetary fines, operational restrictions, and enhanced oversight requirements.
The Establishment of the AML Authority (AMLA)
The creation of the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) represents a cornerstone of the new EU AML framework. AMLA will assume a central role in overseeing and enforcing AML/CFT regulations across the EU. This pivotal shift aims to streamline and enhance the effectiveness of the EU’s fight against money laundering (ML) and terrorist financing (TF).
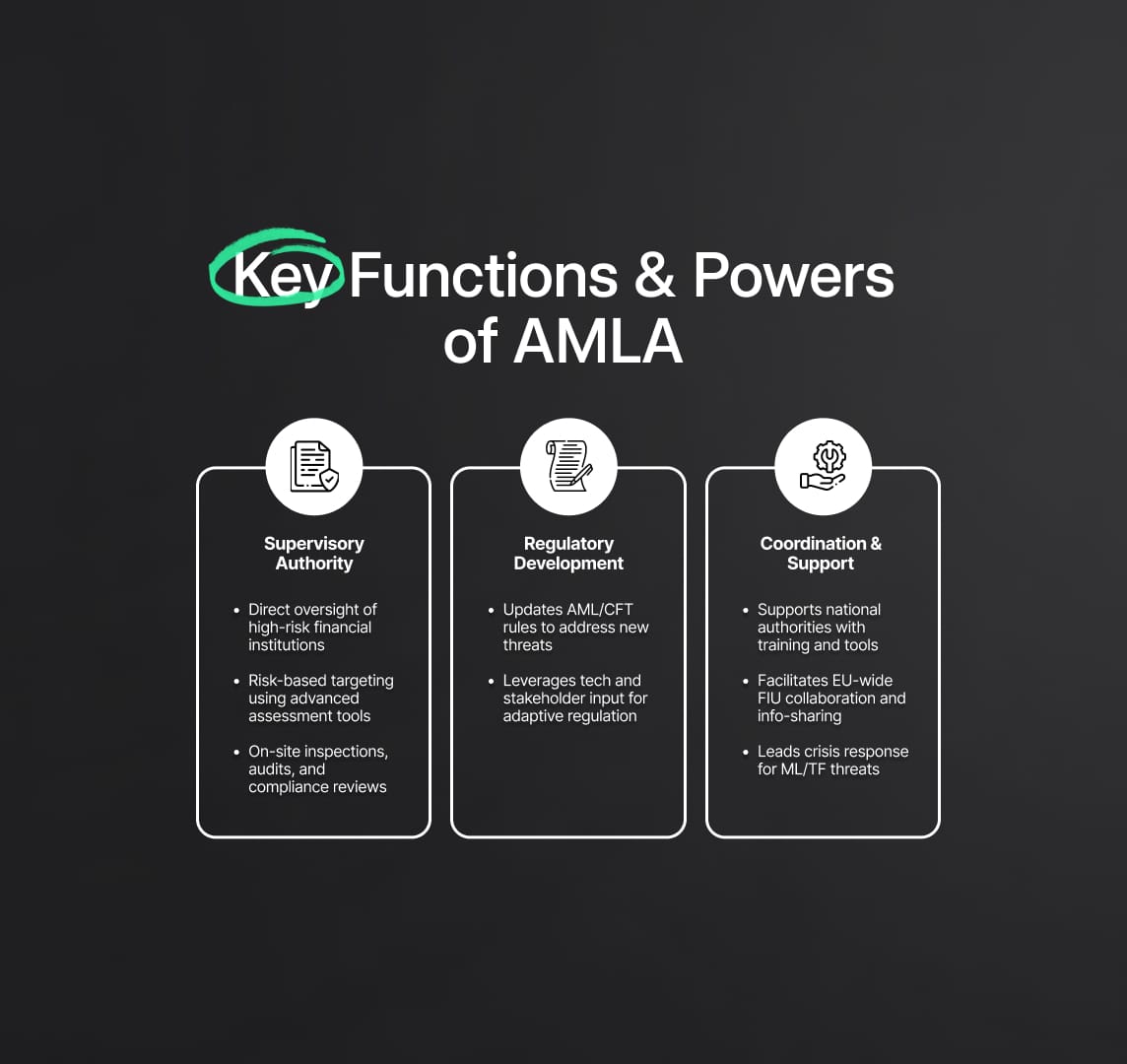
Functions and Powers of AMLA
AMLA's establishment brings several critical functions and powers that will reshape the AML/CFT landscape in Europe. These include direct supervision of high-risk financial institutions, regulatory development, and coordination with national authorities and Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs).
Supervisory Authority
AMLA will have the authority to directly supervise high-risk financial institutions, ensuring they comply with stringent AML/CFT requirements. This direct supervision is crucial for mitigating risks associated with money laundering and terrorist financing, particularly in institutions that operate across borders and are more susceptible to these risks.
- Direct Supervision of High-Risk Entities: AMLA will focus on institutions that pose the highest risks, employing advanced risk assessment tools to identify and monitor these entities. This targeted approach ensures that supervisory efforts are concentrated where they are most needed, enhancing overall compliance and reducing vulnerabilities.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Enforcement: AMLA will implement robust monitoring mechanisms to continuously assess compliance levels and enforce regulations. This includes regular audits, on-site inspections, and detailed reviews of institutions' AML/CFT policies and procedures.
Regulatory Development
AMLA will be responsible for developing and updating AML/CFT regulations to keep pace with evolving threats and emerging technologies. This proactive stance ensures that the regulatory framework remains relevant and effective in addressing new and sophisticated methods of financial crime.
- Adaptive Regulatory Framework: AMLA will continuously evaluate the AML/CFT landscape and introduce new regulations or modify existing ones to address emerging risks. This includes leveraging technology to enhance regulatory measures and adopting innovative solutions to combat ML/TF activities.
- Stakeholder Engagement: AMLA will engage with various stakeholders, including financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and industry experts, to gather insights and feedback. This collaborative approach ensures that regulations are practical, comprehensive, and effective.
Coordination and Support
AMLA will work closely with national authorities to coordinate AML/CFT efforts, provide technical support, and foster information sharing among Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs). This collaborative effort is essential for creating a cohesive and unified AML/CFT regime across the EU.
- National Authority Support: AMLA will offer technical assistance and resources to national authorities, helping them enhance their supervisory capabilities and align with EU-wide standards. This support includes training programs, workshops, and the provision of advanced tools and technologies for AML/CFT supervision.
- Information Sharing and Collaboration: AMLA will facilitate seamless information sharing among FIUs and other relevant bodies, promoting transparency and cooperation. This includes the development of secure communication channels and databases to ensure timely and efficient exchange of information related to ML/TF activities.
- Crisis Management and Response: AMLA will establish protocols for rapid response to emerging threats and financial crime crises. This includes coordinating joint investigations, mobilizing resources, and implementing emergency measures to contain and mitigate risks.
AML Framework: Legislative Background
In 2024, EU co-legislators agreed on a comprehensive AML/CFT package to bolster the fight against financial crime. This legislative overhaul aims to address the growing complexity of money laundering and terrorist financing activities by establishing a unified regulatory framework and creating a dedicated authority to oversee its implementation. The key components of this package include the Regulation Establishing AMLA, the Regulation Establishing a Single AML/CFT Rulebook, and the Revision of the AML/CFT Directive (AMLD6).
Regulation Establishing AMLA (2024/1620)
The Regulation Establishing the Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) is a cornerstone of the new EU AML framework. This regulation outlines the creation of AMLA and its comprehensive mandate to oversee and enforce AML/CFT measures across the EU. The establishment of AMLA marks a significant shift towards centralized supervision, aiming to ensure more consistent and effective enforcement of AML/CFT regulations.
- Centralized Supervision: AMLA will have the authority to directly supervise financial institutions that pose the highest risks of money laundering and terrorist financing. This centralized approach is designed to enhance the effectiveness of AML/CFT measures by ensuring that high-risk entities are subject to stringent oversight.
- Comprehensive Mandate: AMLA's mandate includes developing and updating AML/CFT regulations, coordinating efforts with national authorities, and providing technical support and guidance. This broad mandate ensures that AMLA can address emerging threats and adapt to changes in the financial crime landscape.

Regulation Establishing a Single AML/CFT Rulebook (2024/1624)
The Regulation Establishing a Single AML/CFT Rulebook aims to create a harmonized set of rules that apply uniformly across all Member States. This regulation is designed to eliminate inconsistencies in national AML/CFT regulations and ensure a level playing field across the EU.
- Uniform Standards: The single rulebook establishes uniform standards for AML/CFT measures, including customer due diligence (CDD), risk assessment, and reporting obligations. These standards are designed to ensure that all financial institutions in the EU adhere to the same high level of compliance.
- Simplified Compliance: By harmonizing AML/CFT rules, the single rulebook simplifies compliance for financial institutions operating in multiple Member States. This reduces the regulatory burden and ensures that AML/CFT measures are applied consistently across the EU.
Revision of the AML/CFT Directive (AMLD6 - 2024/1640)
The revision of the AML/CFT Directive, also known as AMLD6, enhances existing provisions and incorporates new measures to address emerging risks and challenges in the fight against financial crime. AMLD6 builds on the foundations of previous directives while introducing several key changes to strengthen the EU's AML/CFT framework.
- Enhanced Risk-Based Approach: AMLD6 places a greater emphasis on a risk-based approach to AML/CFT measures. This approach allows financial institutions to tailor their AML/CFT controls based on the specific risks they face, ensuring more effective and efficient compliance.
- Expanded Scope: The directive expands the scope of AML/CFT measures to include new sectors and activities that are vulnerable to money laundering and terrorist financing. This includes virtual asset service providers (VASPs), real estate agents, and other non-financial businesses and professions.
- Strengthened Cooperation: AMLD6 promotes greater cooperation and information sharing among national authorities, financial institutions, and FIUs. This enhanced collaboration is crucial for detecting and preventing financial crime in a globalized economy.
Implications for Financial Institutions
The new AML/CFT package has significant implications for financial institutions operating within the EU. Institutions must adapt to new regulatory requirements, enhance their AML/CFT systems, and ensure compliance with stricter oversight.
Ongoing Contributions to the AML Framework/Anti-Money Laundering Regime
As the transition to the newly established Anti-Money Laundering Authority (AMLA) progresses, the European Banking Authority (EBA) continues to play a crucial role in shaping and enhancing the EU's AML/CFT regime. The European Commission has entrusted the EBA with providing technical advice on several critical aspects to ensure the new framework is robust and effective. Here, we delve deeper into these areas to understand their significance and technical details.
Methodology for Assessing ML/TF Risk
The EBA is developing a comprehensive and standardised methodology for EU supervisors to assess the money laundering (ML) and terrorist financing (TF) risks of financial institutions. This methodology is designed to ensure consistency and accuracy in risk evaluations across the EU.
- Risk Assessment Framework: The framework incorporates various quantitative and qualitative metrics to evaluate the risk profile of financial institutions. These metrics include transaction volumes, customer profiles, geographical exposure, and historical compliance records.
- Dynamic Risk Scoring: Institutions will be assigned dynamic risk scores based on real-time data and periodic reviews. This approach allows for continuous monitoring and timely adjustments to risk assessments.
- Advanced Analytics and AI: The EBA is exploring the use of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance the precision of risk assessments. AI can help identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential ML/TF activities, providing supervisors with actionable insights.
Selection of Directly Supervised Institutions
Identifying institutions that require direct supervision by AMLA is a critical task. The EBA is formulating a methodology to determine which financial institutions pose the highest risks and therefore warrant closer scrutiny.
- Criteria for Selection: The selection criteria include factors such as the size of the institution, the complexity of its operations, its customer base, and its exposure to high-risk jurisdictions. Institutions with significant cross-border activities are likely to be prioritized.
- Risk-Based Supervision: The EBA emphasizes a risk-based approach, where resources are allocated based on the risk levels of institutions. High-risk institutions will undergo more frequent and detailed examinations, ensuring that supervisory efforts are focused where they are most needed.
- Supervisory Coordination: The methodology ensures seamless coordination between AMLA and national supervisory authorities. This includes sharing information and collaborating on supervisory activities to avoid duplication of efforts and ensure comprehensive oversight.
Customer Due Diligence Standards
Uniform customer due diligence (CDD) standards are essential for effective AML/CFT compliance across the EU. The EBA is working on establishing these standards to ensure thorough and effective verification processes.
- Standardized Procedures: The EBA's guidelines will detail the specific steps financial institutions must take during the CDD process, including identity verification, risk assessment, and ongoing monitoring. These procedures aim to create a consistent approach to CDD across the EU.
- Enhanced Verification Techniques: The standards will incorporate advanced verification techniques, such as biometric identification and digital onboarding solutions, to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the CDD process.
- Risk-Based Customer Profiling: Financial institutions will be required to implement risk-based customer profiling, where the level of due diligence performed is commensurate with the risk posed by the customer. High-risk customers will undergo more rigorous scrutiny.
Sanctions and Administrative Measures
Defining criteria for determining pecuniary sanctions and administrative measures for AML/CFT breaches is vital for ensuring proportionality and deterrence. The EBA's work in this area aims to create a fair and effective enforcement framework.
- Graduated Sanctions: The EBA is developing a system of graduated sanctions that considers the severity and frequency of AML/CFT breaches. Minor infractions may result in warnings or fines, while serious or repeated violations could lead to substantial penalties or license revocations.
- Transparent Enforcement: The criteria for sanctions will be transparent and publicly available, ensuring that financial institutions understand the potential consequences of non-compliance. This transparency is expected to promote greater adherence to AML/CFT regulations.
- Deterrence and Compliance Incentives: The EBA's framework aims to strike a balance between deterrence and incentivizing compliance. Sanctions will be designed to discourage non-compliance, while measures will also be in place to reward institutions that demonstrate strong AML/CFT controls and proactive risk management.
Key Actions for Financial Institutions
To navigate these changes effectively, financial institutions need to take proactive steps to strengthen their AML/CFT frameworks. Here are the key actions institutions should focus on:
AML/CFT Programs
- Policy and Procedure Updates: Financial institutions must review and update their AML/CFT policies and procedures to align with the new regulatory expectations. This includes incorporating the latest guidelines and requirements set forth by AMLA and the EBA.
- Comprehensive Review: Conduct a thorough review of existing policies to identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Integration of New Standards: Integrate the latest AML/CFT standards and best practices into the institution's framework.
- Documentation: Ensure all changes are well-documented and communicated to relevant stakeholders.
- Enhanced Training Programs: Staff training is crucial for effective AML/CFT compliance. Institutions need to develop comprehensive training programs that cover the new regulations, risk assessment methodologies, and compliance obligations.
- Regular Training Sessions: Implement regular training sessions to keep staff updated on the latest AML/CFT developments.
- Role-Specific Training: Tailor training programs to different roles within the institution to ensure that all employees understand their specific responsibilities.
- Assessment and Certification: Incorporate assessments and certification processes to ensure that staff have a solid understanding of AML/CFT requirements.

Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
- Comprehensive Information Collection: Institutions need to collect detailed and comprehensive CDD information to effectively monitor customer activities and detect suspicious transactions.
- Customer Identification: Implement robust customer identification procedures, including verifying customer identities using reliable, independent sources.
- Risk Profiling: Develop detailed risk profiles for each customer based on their transaction patterns, geographical location, and other relevant factors.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Establish continuous monitoring processes to detect changes in customer behavior and update risk profiles accordingly.
- Advanced Verification Techniques: Leverage advanced technologies and tools to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of the CDD process.
- Biometric Identification: Utilize biometric identification methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, to verify customer identities.
- Digital Onboarding Solutions: Implement digital onboarding solutions to streamline the CDD process and reduce the risk of identity fraud.
- Data Analytics: Use data analytics to identify patterns and anomalies in customer transactions that may indicate potential ML/TF activities.
Direct Supervision
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: High-risk institutions identified for direct EU-level supervision should conduct comprehensive risk assessments and implement robust risk mitigation strategies.
- Detailed Risk Assessments: Perform detailed risk assessments to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas of non-compliance.
- Risk Mitigation Plans: Develop and implement risk mitigation plans to address identified vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with AML/CFT regulations.
- Regular Audits and Reviews: Conduct regular internal audits and reviews to ensure ongoing compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Compliance Obligations: Institutions under direct supervision must ensure they meet all compliance obligations set by AMLA.
- Regulatory Reporting: Establish processes for timely and accurate regulatory reporting, including suspicious activity reports (SARs) and other required disclosures.
- Collaboration with Supervisory Authorities: Maintain open communication and collaboration with supervisory authorities to ensure compliance and address any issues promptly.
- Enhanced Internal Controls: Strengthen internal controls and governance frameworks to support compliance efforts and reduce the risk of ML/TF activities.
Reduce your
compliance risks


