MiCA Regulation: Guidelines for Crypto-Asset Classification
ESAs introduce MiCA Regulation guidelines with templates and tests, ensuring consistent crypto-asset classification across the EU and enhancing transparency for investors.

The European Supervisory Authorities (ESAs) have issued detailed guidelines under Article 97(1) of the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCAR), focusing on standardizing the classification and regulatory treatment of crypto-assets. This update includes templates for legal opinions and explanations, along with a standardized test for determining whether assets fall under MiCAR’s scope. The guidelines aim to harmonize regulatory practices across the EU, reduce inconsistencies, and prevent regulatory arbitrage. These measures enhance market transparency, protect investors, and ensure a level playing field for crypto-asset providers, fostering greater trust and stability in the European crypto-asset ecosystem.
Source
[1]
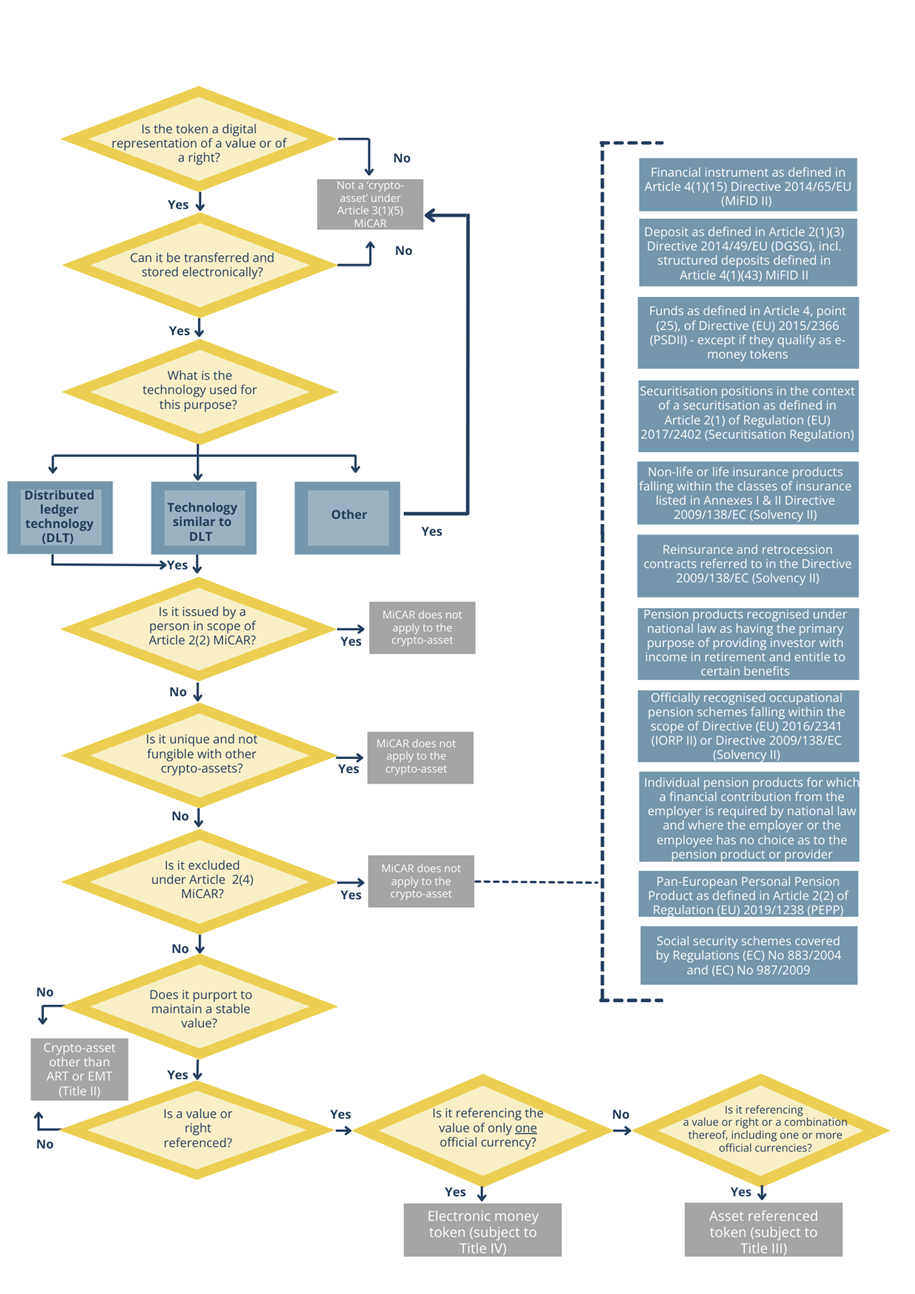
[2]

Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) Compliance Updates
The MiCA Regulation aims to establish a comprehensive framework for regulating crypto-assets in the EU. The latest guidelines from the ESAs focus on three critical areas:
1. Standardized Templates for Compliance
The ESAs have introduced two key templates to streamline compliance:
- Explanations Template: This is required for white papers accompanying crypto-assets that do not qualify as ARTs (Asset-Referenced Tokens) or EMTs (E-money Tokens). It ensures that market participants explain why their crypto-assets are not within these categories or excluded from MiCAR.
- Legal Opinions Template: Required for ARTs, this template mandates issuers to provide a legal opinion validating their classification under MiCAR.
These templates address the challenges of inconsistent regulatory submissions by ensuring uniformity and clarity in the documentation provided to national authorities.
Key Details of the Templates:
- Structured Fields: Both templates include structured fields for the regulatory classification of crypto-assets, covering aspects such as fungibility, value references, and compliance with Article 8(4), Article 17(1), and Article 18(2) of MiCAR.
- Flexibility for Complexity: While the templates are detailed, they also allow flexibility to account for the complexity of some crypto-assets, enabling issuers to include annexes for additional information.
2. Standardized Test for Classification
The standardized test provides a clear pathway for determining whether a crypto-asset falls under MiCAR’s scope. The test focuses on:
- Whether the asset is unique and non-fungible.
- Its alignment with financial instruments, deposits, or other regulated products as defined in Article 2(4) of MiCAR.
- Exclusions under Article 2(2), such as assets issued by central banks or used for internal purposes by organizations.
This test facilitates a consistent approach to classification across EU member states, reducing ambiguity and enhancing regulatory convergence.
3. Expanded Scope and Definitions
MiCAR provides a robust framework for ARTs and EMTs, but the new guidelines also clarify the treatment of other crypto-assets, including:
- Hybrid Tokens: These require a case-by-case analysis to determine their classification.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): While generally excluded, NFTs with characteristics overlapping with ARTs or EMTs may be subject to MiCAR.
- Decentralized Assets: Even assets without identifiable issuers (e.g., Bitcoin) fall under MiCAR if they meet the defined criteria.
4. Implementation Timeline and Next Steps
The guidelines become effective two months after publication in all official EU languages. During this period, stakeholders are expected to prepare for compliance by revising their internal policies, processes, and documentation to align with the new requirements.
5. Feedback and Flexibility
The ESAs incorporated feedback from public consultations, adding flexibility in areas like hybrid tokens and templates. These refinements address stakeholder concerns while maintaining the integrity of MiCAR’s objectives.

MiCAR Updates: Implications for Stakeholders
The updates to the MiCA Regulation carry profound implications for different stakeholders, requiring proactive steps to ensure compliance and address emerging challenges.
1. For Market Participants (Issuers and Service Providers)
What They Need to Do
- Comply with Templates: Issuers must use the explanation and legal opinion templates to document their asset classifications accurately.
- Conduct Detailed Assessments: A comprehensive analysis is needed to determine whether an asset falls within MiCAR’s scope, including its classification as an ART, EMT, or other crypto-asset.
- Adapt Internal Processes: Update compliance frameworks and establish robust documentation practices to align with MiCAR requirements.
Challenges
- Complexity of Classifications: The requirement for case-by-case assessments for hybrid tokens and NFTs can be resource-intensive.
- Solution: Engage external legal and technical experts to streamline classifications.
- High Compliance Costs: Small issuers may find the costs of legal opinions and regulatory filings burdensome.
- Solution: Explore consortia or shared compliance solutions to reduce individual expenses.
2. For Supervisory Authorities
What They Need to Do
- Harmonize Regulatory Practices: Authorities must adopt the standardized templates and test to ensure consistent enforcement across member states.
- Train Staff: Build expertise in applying MiCAR’s guidelines, particularly for complex cases like hybrid tokens and decentralized assets.
Challenges
- Resource Allocation: Increased data and documentation from stakeholders may strain supervisory resources.
- Solution: Implement automated tools and AI systems to assist in reviewing submissions.
- Interpreting Complex Cases: Assessing hybrid tokens or NFTs requires nuanced understanding.
- Solution: Develop case databases and collaborate with other authorities to share insights.
3. For Consumers and Investors
What They Need to Do
- Stay Informed: Educate themselves on the implications of MiCAR classifications, particularly regarding the risks associated with different types of crypto-assets.
- Evaluate Providers: Choose issuers and service providers that demonstrate clear compliance with MiCAR guidelines.
Challenges
- Understanding New Classifications: The nuances of MiCAR classifications may be confusing for non-experts.
- Solution: Rely on simplified disclosures mandated by the guidelines, which aim to enhance consumer understanding.
- Potential Delays in Offerings: Issuers adjusting to new requirements may slow down the release of certain products.
- Solution: Advocate for timely updates and clear communication from providers.
4. For Legal and Compliance Professionals
What They Need to Do
- Draft Legal Opinions: Provide comprehensive and conflict-free legal opinions for ARTs and EMTs.
- Advise on Classification: Assist clients in applying the standardized test and using the templates accurately.
Challenges
- Navigating Diverse Jurisdictions: Variations in national interpretations of MiCAR may complicate compliance.
- Solution: Build expertise in EU-wide regulations and collaborate with local counsel where necessary.
- High Demand for Expertise: Increased need for legal opinions may lead to resource constraints.
- Solution: Adopt scalable processes and leverage technology to manage workloads.
Regulatory Trends in Crypto-Assets Regulation
The updates to the Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCAR) establish a strong foundation for harmonized regulation across the EU. These guidelines are just the beginning of a broader regulatory journey as the crypto-asset ecosystem evolves.
Future regulatory efforts will likely address challenges posed by decentralized finance (DeFi), tokenized assets, and increasingly hybrid financial instruments. Supervisory authorities may also introduce more granular guidance to keep pace with innovation and strengthen international collaboration to oversee global crypto transactions effectively.
Another anticipated trend is the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into crypto regulations, reflecting the EU’s commitment to sustainability. Additionally, as crypto adoption grows among consumers, ensuring transparency and accessibility will become critical priorities.
MiCAR’s framework positions the EU to lead in shaping a secure, transparent, and innovative crypto-asset market. Stakeholders must remain adaptable to align with future regulatory developments and capitalize on emerging opportunities in this dynamic space.
Reduce your
compliance risks



